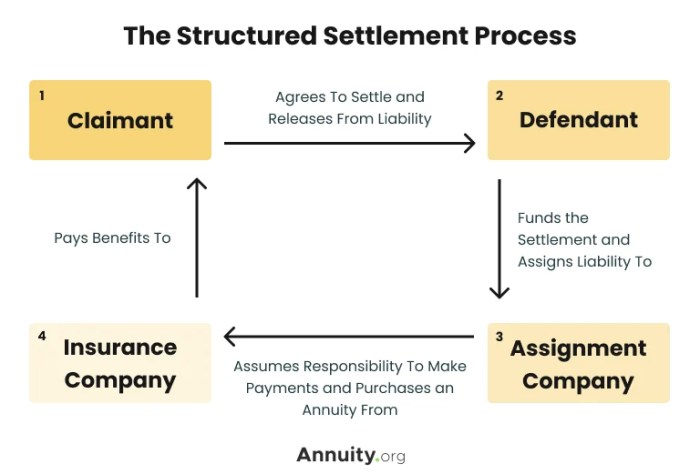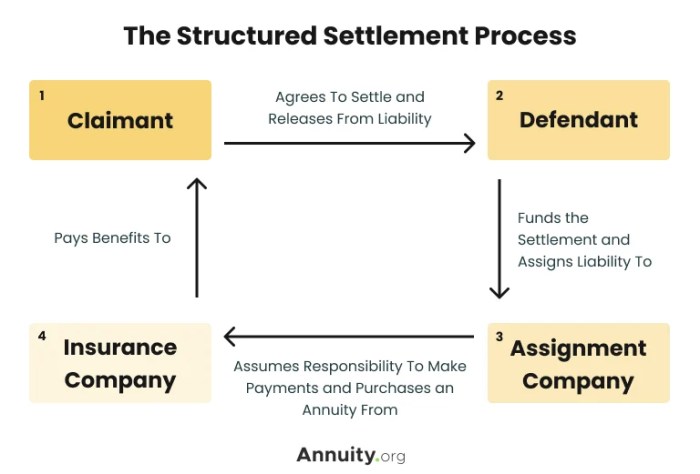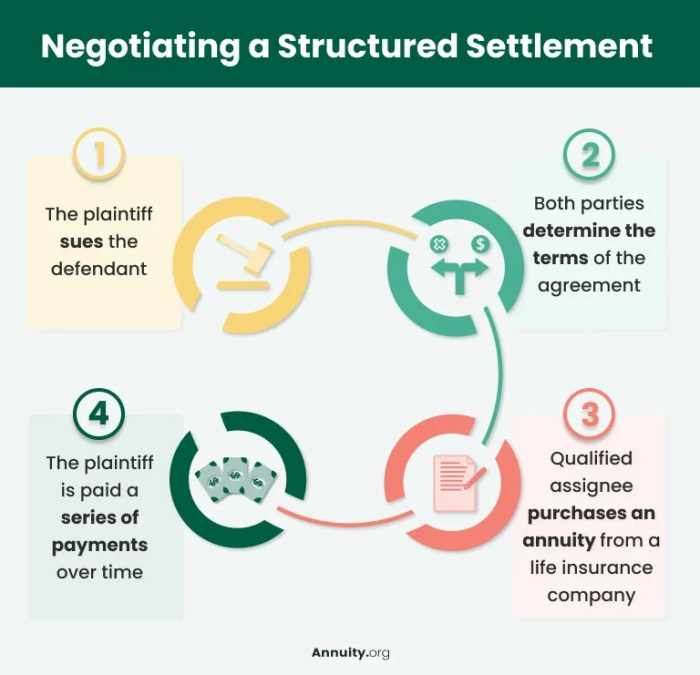
Navigating the complexities of a structured settlement can feel like entering a labyrinth of legal and financial jargon. But understanding the terms and conditions is crucial for making informed decisions about your future. Whether you’re a recipient of a structured settlement or someone considering this option, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to confidently navigate this landscape.
Structured settlements, often used in personal injury cases, offer a unique alternative to lump-sum payments. Instead of receiving a single large sum, you receive regular payments over a specified period. This can provide financial stability and peace of mind, but it also comes with its own set of considerations. By understanding the key terms, payment structures, legal framework, and financial implications, you can make well-informed choices that align with your individual circumstances and goals.
Key Terms in Structured Settlement Agreements
Understanding the terms used in a structured settlement agreement is crucial for making informed decisions about your future financial security. These terms define the structure of your payments and ultimately determine the overall value of your settlement.
Annuity
An annuity is a financial product that provides a series of regular payments over a set period of time. In a structured settlement, the annuity acts as a contract between the settlement provider and the recipient, guaranteeing a stream of payments for a specified duration.
Periodic Payments
Periodic payments refer to the regular installments of money that you receive under a structured settlement. These payments can be made monthly, quarterly, annually, or at other intervals, depending on the terms of the agreement. The frequency and amount of each payment are determined by the structure of the annuity and the present value of the settlement.
Present Value
The present value represents the current worth of a future stream of payments. It takes into account the time value of money, meaning that money received today is worth more than the same amount received in the future due to factors like inflation and potential investment opportunities. In structured settlements, the present value reflects the total amount of money that the settlement provider is committing to pay over the life of the annuity.
Discount Rate
The discount rate is a percentage used to calculate the present value of future payments. It reflects the risk associated with the investment and the opportunity cost of receiving money later rather than sooner. A higher discount rate implies a lower present value for future payments, as the money is discounted at a faster rate.
The present value of a structured settlement is calculated by discounting the future payments at the agreed-upon discount rate.
For example, imagine a structured settlement that promises to pay $10,000 annually for 10 years. If the discount rate is 5%, the present value of the settlement would be less than $100,000, as the future payments are discounted at a rate of 5% per year. This means that the settlement provider is effectively paying less than $100,000 today in exchange for making payments of $10,000 per year for the next 10 years.
Discount Rate in Real-World Scenarios
The discount rate used in structured settlements can vary based on several factors, including the risk profile of the settlement provider, the prevailing interest rates in the market, and the length of the payment period.
For example, a structured settlement with a longer payment period might have a higher discount rate compared to a settlement with a shorter payment period.
This is because the settlement provider faces a greater risk of unforeseen circumstances affecting their ability to make payments over a longer duration.
Understanding the Structure of Payments
Structured settlements provide a flexible framework for receiving compensation, offering various payment structures to meet individual needs and circumstances. These structures are designed to ensure the recipient receives consistent financial support over time, potentially helping manage long-term care costs and financial stability.
Payment Schedules
Structured settlements offer different payment schedules to cater to individual needs and circumstances. Understanding these schedules can help recipients make informed decisions regarding their financial planning and long-term financial security.
- Lump-sum payments: A single, upfront payment of the entire settlement amount. This option provides immediate access to a large sum of money, which can be beneficial for immediate expenses, investments, or debt consolidation. However, it can also lead to financial mismanagement if not carefully planned.
- Periodic payments: Regular payments made over a predetermined period, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. This structure offers consistent income, potentially providing long-term financial stability. It can be particularly beneficial for managing recurring expenses, such as medical bills or living costs, and for ensuring financial security over time.
- Combination of lump-sum and periodic payments: A blend of both payment structures, allowing recipients to receive a portion of the settlement upfront while also receiving regular payments. This option can provide immediate financial relief while ensuring ongoing income for future needs.
Factors Influencing Payment Structure
Several factors influence the frequency and duration of structured settlement payments, ensuring the structure aligns with the recipient’s needs and circumstances.
- Severity of the injury: The severity of the injury plays a significant role in determining the payment structure. More severe injuries often result in larger settlements and longer payment durations, providing financial support for ongoing medical care and rehabilitation.
- Age of the recipient: The recipient’s age is another critical factor. Younger recipients may receive longer payment durations to ensure financial support throughout their lives, especially if they have significant medical needs or are unable to work. Older recipients may opt for shorter durations, focusing on immediate needs and potential estate planning considerations.
Impact on Financial Planning
The chosen payment structure significantly impacts financial planning and long-term financial stability. It is crucial to consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of each structure and choose the one that aligns with individual needs and circumstances.
| Payment Structure | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Lump-sum payment | Immediate access to a large sum of money, flexibility in managing funds | Risk of financial mismanagement, potential for early depletion of funds |
| Periodic payments | Consistent income, long-term financial stability, potential for managing recurring expenses | Limited access to a large sum of money upfront, potential for lower overall settlement value due to time value of money |
| Combination of lump-sum and periodic payments | Immediate financial relief, ongoing income, balance between immediate needs and long-term financial security | May require careful planning to manage both upfront and periodic payments |
Legal and Financial Considerations

Structured settlements are subject to a complex legal framework that ensures fairness and transparency for all parties involved. Understanding the legal and financial aspects of structured settlements is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing their benefits.
Legal Framework
The legal framework governing structured settlements involves a combination of federal and state laws, regulations, and court decisions. The primary federal legislation governing structured settlements is the Structured Settlement Protection Act (SSPA). This act protects the rights of structured settlement recipients by regulating the transfer of structured settlement payments. The SSPA establishes a process for approving structured settlement transfers, ensuring that recipients are fully informed and understand the implications of selling their future payments.
The SSPA also sets forth specific requirements for settlement brokers, including licensing and disclosure obligations. State laws further regulate structured settlements, often mirroring or expanding upon the provisions of the SSPA. These state laws may address issues such as the qualifications of settlement brokers, the disclosure of fees, and the rights of recipients to reject or revoke transfers.
Role of Courts, Insurance Companies, and Settlement Brokers
Courts play a crucial role in approving structured settlements, ensuring they are fair and equitable to both parties. Insurance companies are responsible for funding structured settlements, making periodic payments to recipients as Artikeld in the agreement. Settlement brokers facilitate the transfer of structured settlements, connecting recipients with potential buyers and assisting with the legal and financial aspects of the transaction.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Structured settlements, while offering numerous benefits, also come with inherent risks and challenges. These include:
- Inflation: The purchasing power of future payments may be eroded by inflation, making them less valuable over time.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Changes in interest rates can impact the present value of future payments, affecting the overall financial benefit of the settlement.
- Tax Implications: Payments from structured settlements may be subject to federal and state income taxes, reducing the net amount received by the recipient.
- Early Death: If the recipient dies before receiving all payments, the remaining payments may be forfeited or subject to specific provisions in the settlement agreement.
- Change in Circumstances: Unforeseen events, such as a change in financial needs or health status, may make the original structured settlement terms less desirable.
Managing Structured Settlements

A structured settlement is a long-term financial agreement that provides regular payments over time. Managing these settlements effectively is crucial to ensure financial security and achieve your long-term financial goals. Proper planning and management can help you maximize the value and benefits of your structured settlement.
Financial Planning and Management
Financial planning is essential for managing structured settlements effectively. It involves creating a budget, setting financial goals, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. By understanding your financial situation and future needs, you can make informed decisions about how to use your structured settlement funds.
- Create a Budget: A budget helps you track your income and expenses, ensuring you stay on track with your financial goals. It allows you to allocate funds for essential needs, savings, and investments.
- Set Financial Goals: Establishing clear financial goals, such as saving for retirement, paying off debt, or funding education, provides direction and motivation for managing your structured settlement funds.
- Develop a Financial Strategy: Based on your goals and risk tolerance, develop a comprehensive financial strategy that Artikels how you will manage your structured settlement funds. This may involve investing, saving, or a combination of both.
Maximizing Value and Benefits
Several strategies can help you maximize the value and benefits of your structured settlement. These strategies involve leveraging the structure of the payments to achieve your financial objectives.
- Investing: Investing a portion of your structured settlement funds can help grow your wealth over time. You can choose from various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, depending on your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Saving: Setting aside a portion of your structured settlement funds in a savings account provides a safe and accessible source of funds for emergencies or future needs. You can consider opening a high-yield savings account or a certificate of deposit (CD) to earn interest on your savings.
- Budgeting: A well-structured budget helps you allocate your structured settlement funds efficiently, ensuring you have enough for essential expenses, savings, and investments.
Tools and Resources
Various tools and resources are available to assist individuals in managing their structured settlements. These resources can provide guidance, support, and access to financial expertise.
- Financial Advisors: Financial advisors can provide personalized financial advice, develop customized investment strategies, and help you manage your structured settlement funds effectively.
- Settlement Administrators: Settlement administrators are responsible for managing the disbursement of structured settlement payments. They can provide information about your settlement, answer questions about your payments, and assist with any changes or modifications to your settlement agreement.
- Online Tools and Calculators: Several online tools and calculators can help you estimate the future value of your structured settlement, project your financial needs, and create a budget. These tools can provide valuable insights and support for managing your settlement funds.
As you embark on your journey with a structured settlement, remember that knowledge is power. By carefully reviewing the terms and conditions, understanding the various aspects of payment structures, and considering the legal and financial implications, you can confidently navigate this unique financial arrangement. Whether you choose to manage the settlement yourself or seek guidance from a financial advisor, the insights gained from this exploration will empower you to make informed decisions that support your long-term financial well-being.
FAQ Insights
Can I change the payment schedule of my structured settlement?
It’s possible to modify the payment schedule, but it often requires court approval and may be subject to certain restrictions. Consult with a legal professional to explore your options.
What happens to my structured settlement if I pass away?
The terms of your structured settlement agreement will Artikel the disposition of the remaining payments. This may involve payment to your beneficiaries or a designated estate.
Are there any tax implications for receiving structured settlement payments?
Yes, structured settlement payments may be subject to taxes. Consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax implications in your situation.
Can I sell my structured settlement for a lump-sum payment?
Yes, you can sell your structured settlement to a third-party company for a lump-sum payment. However, these transactions are often subject to significant discounts and fees.